Explore chapters on persistent left superior vena cava, aberrant right subclavian artery, double aortic arch and right aortic arch.
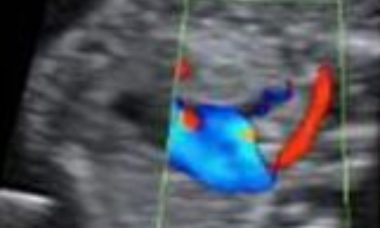
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery
The right subclavian artery (RSA) normally branches from the brachiocephalic artery, which is the first of the 3 aortic arch vessels. The RSA is positioned to the left of the trachea/esophagus and it is directed to the right arm, passing anteriorly to these anatomic structures.
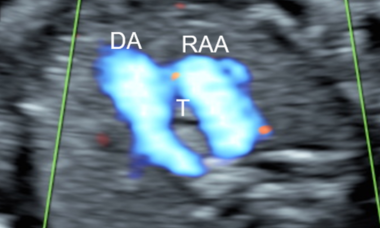
Right Aortic Arch
Right aortic arch (RAA) is an arch sidedness anomaly. Normally, left aortic arch (LAA) courses to the left of the trachea, over the left mainstem bronchus while RAA courses to the right of the trachea, over the right mainstem bronchus. Some variants of RAA cause a vascular ring around the trachea and esophagus.
Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava (PLSVC)
Persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) represents the most common form of anomalous systemic venous return resulting from in utero failure of the regression of the left anterior and common cardinal veins.
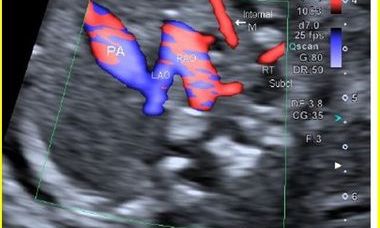
Double Aortic Arch
Double aortic arch (DAA) is a form of vascular ring found in approximately 0.005%- 0.007% of fetuses where the trachea and esophagus are surrounded in the form of a circle by the right and left aortic arches.