Explore chapters on Tetralogy of Fallot, Pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect and Absent pulmonary valve syndrome.
Tetralogy of Fallot
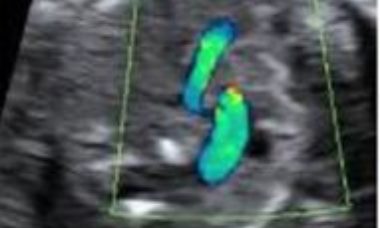
Tetralogy of Fallot is a cono-truncal anomaly that is featured by the combination of a subaortic ventricular septal defect, aortic valve overriding the defect, infundibular pulmonic stenosis and hypertrophy of the right ventricle; hypertrophy of the right ventricle however only develops after birth.
Pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect
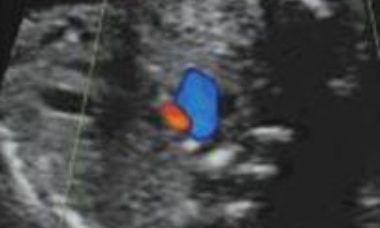
This is a variant of tetralogy of Fallot that is present in about 10% of cases and is characterized by atresia of the main pulmonary artery. Many anatomical variations have a major impact on the final outcome: the pulmonary circulation can be supplied in a retrograde manner by the ductus arteriosus.
Absent pulmonary valve syndrome
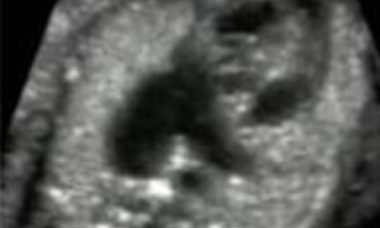
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome is a cardiac abnormality characterized by dysplasia or or absence of the pulmonary valve, associated in most instances with severe dilatation of the pulmonary trunk and branches. In most cases, this condition is found with tetralogy of Fallot and absence of the arterial duct.