Supplement your learning for ISUOG's education course on emergency gynecology.
Learning Objectives:
- Gain expertise in ultrasound diagnosis of adnexal torsion
- Gain expertise in ultrasound diagnosis and management of inflammatory disease in the pelvis and the bowel
- Gain and improve knowledge of ultrasound role in acute on chronic pelvic pain in endometriosis
- Improve knowledge on ultrasound diagnostics in case of heavy vaginal bleeding in pregnant women
- Gain knowledge on the role of ultrasound in case of massive peritoneum in pregnant and non-pregnant women
- Gain knowledge on the role of interventional radiology in acute gynecological patients
- Gain knowledge on the role of ultrasound in postoperative complications
Explore the topic before you attend our course:
In order to make the most of this learning experience and help you achieve your learning objectives, we have prepared a path to guide you from the essentials to our course’s topics through ISUOG resources. The material below, will take you from the most basics to a more comprehensive view of Emergency Gynecology, some open to everyone and some available only to ISUOG members –some may even grant you CME points:
Some of these activities are exclusively available to our members. Become a member today.
VISUOG
Cervical Ectopic Pregnancy
Cervical ectopic pregnancy refers to an abnormal implantation of a fertilized ovum within the myometrium below the level of the internal os with a reported incidence of less than 1% of all ectopic pregnancies.
Intramural Ectopic Pregnancy
Intramural ectopic pregnancy refers to an abnormal implantation of a pregnancy within the myometrium. A gestational sac extending beyond the endometrial-myometrial junction is the defining feature. Intramural ectopic pregnancies should be subdivided into partial and complete. Ultrasound is the first-hand diagnostic tool.
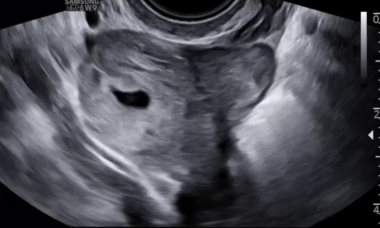
Cervico-isthmic Pregnancy
A cervico-isthmic pregnancy is a rare condition defined by implantation of the gestational sac between the anatomical and histological internal os. Unlike true cervical pregnancies, it has the ability to develop beyond the second trimester.
Salpingitis
Salpingitis is defined as an infection and inflammation in the oviducts which act as the site for the transport of ova, sperm, and the site of fertilization and early embryonic development.
Ovarian Ectopic Pregnancy
Ovarian ectopic pregnancy (OEP) is a rare type of ectopic pregnancy in which the fertilized ovum implants into the ovary.
Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is defined as the presence of a pregnancy outside the uterine cavity, the commonest location being the fallopian tube. They account for 1-2% of pregnancies in the UK and may be as high as 4% with assisted conception.
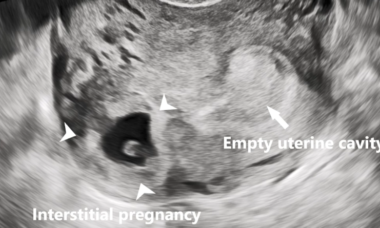
Interstitial Ectopic Pregnancy
Interstitial ectopic pregnancy is defined as the ectopic gestation implanting in the most proximal part of the fallopian tube.
Abdominal pregnancy
An abdominal ectopic pregnancy ( AP) is a pregnancy that occurs in the abdominal cavity outside of the female reproductive organs.
Cesarean Scar Pregnancy
Cesarean scar pregnancy (CSP) is an abnormal implantation of the gestational sac in the area of the prior caesarean delivery (CD) scar, potentially leading to life-threatening complications, including severe haemorrhage, uterine rupture and development of placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) disorders.
Isolated fallopian tube torsion
Isolated fallopian tube torsion is defined as rotation of the fallopian tube around its longitudinal axis with preserved normal ovary. Isolated fallopian tube torsion is a rare cause of acute pelvic pain in female patients, with estimated incidence of about one in 1.5 million females.
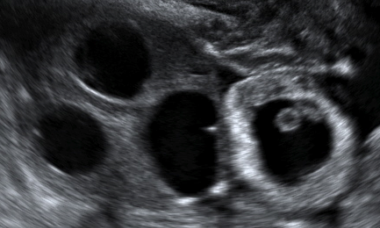
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is usually an iatrogenic complication of assisted reproduction technology but can occur spontaneously in rare cases due to the high production of endogenous gonadotropins, beta-hCG level, gonadotropin-like molecules, or due to enhanced sensitivity to endogenous gonadotropins such as mutations follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) receptor.
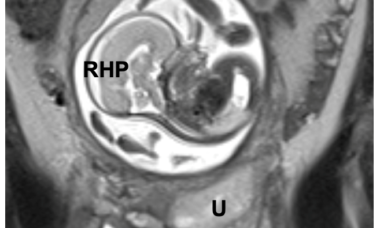
Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy
Unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn is a rare Müllerian anomaly that has a high incidence of obstetric complications such as ectopic pregnancy in the rudimentary horn.